The thought of having cancer is scary, but the importance of being tested regularly can’t be overstated. This is especially true for those with risk factors for a specific type of cancer. Affiliated Dermatology® sees many patients who are concerned they may have skin cancer. Many people who come into our office assume that blood tests are the standard way to diagnose skin cancer. But does skin cancer show up in blood work? In reality, blood tests aren’t a common part of skin cancer detection. To help you better understand the process, we’ve put together this simple guide to skin cancer testing.
Skin Cancer Testing
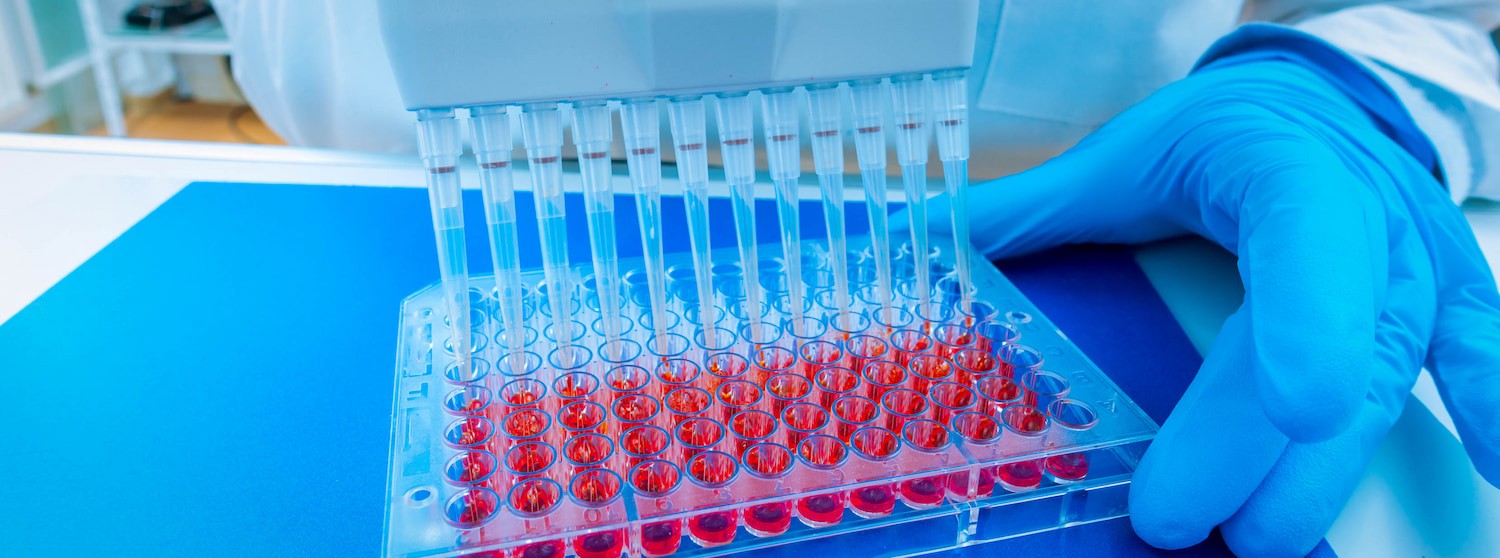
Instead, the process starts with a simple skin examination. A dermatologist will meticulously examine the skin, looking for anything that looks suspicious. If any skin lesions or other anomalies seem as though they warrant further investigation, the tests will continue to the next phase. To further test a suspicious area of skin, a biopsy is performed. During this procedure, a small amount of the skin is removed and sent to a lab for testing. Depending on the area in question, removal comes in various forms. For all of them, the skin will be numbed to ensure patient comfort. The most common types of biopsy are:
- Shave Biopsy – This removes a layer from the skin, similar to shaving.
- Punch Biopsy – A circular tool is used to remove a portion of the skin, allowing for a deeper sample.
- Scalpel Biopsy – A scalpel is used to remove some of the skin. In some cases, the entire suspicious area may be removed.
If the biopsy comes back with a confirmation of skin cancer, additional tests might be used to confirm the extent of the condition. These can range from a closer examination of the lymph nodes to various imaging techniques. Depending on the type of cancer found, skin cancer blood tests might be called for at this stage.
Risk Factors With Skin Cancer
Earlier, we mentioned that the importance of regular testing goes up for those with risk factors for skin cancer. Let’s talk a little bit more about what those are:
- Exposure to UV rays: Too much time in the sun or artificial UV light without protection is a significant risk factor.
- Skin that easily burns, freckles, or reddens: If your skin is already sensitive to UV light, the risk goes up.
- A history of cancer: Both a personal or familial history of cancer puts you at greater risk.
- Moles: Although most are harmless, certain types of moles can be a sign of skin cancer.
- Age: Your risk of getting skin cancer goes up as you age.
- Eye or hair color: Surprisingly, those with blue or green eyes and those with blond or red hair are at higher risk.
Treatments for Skin Cancer
If the entire suspicious area of the skin was removed during the biopsy, it’s possible that no further treatment is necessary. If not, simply removing the remaining portion may be sufficient. This can be done by cutting, similar to the way the biopsy was performed, or by freezing the affected area. A particular variant of this process is called Mohs surgery. This procedure involved a dermatologist at Affiliated Dermatology® removing skin layer by layer and examining it under a microscope. This allows for the complete removal of the cancer while preserving as much skin as possible for cases where the cancer is in a large or highly visible area. In some cases, treatments common for other forms of cancer, such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy, may be used instead. Whatever the case may be, we will discuss all options if signs of any cancer are discovered.
Affiliated Dermatology Can Answer Your Questions About Skin Cancer
At Affiliated Dermatology®, we’ve treated many patients who have or think they may have skin cancer. If this describes you, we know how stressful and worrying it can be. Remember, catching the cancer early is the best way to stay safe. If you have any questions about the testing or treatment processes or anything else related to skin cancer, please reach out to us. We’ll provide you with the information you need to safeguard your health. You can schedule your appointment by texting (480) 405-3877.
Image Credit: luchschenF / Shutterstock